Penetration from high to low density physics law
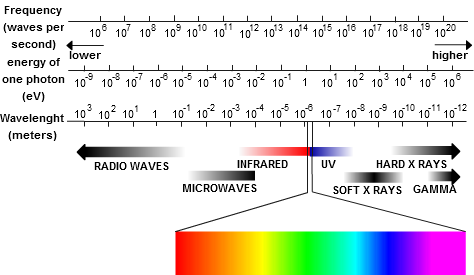

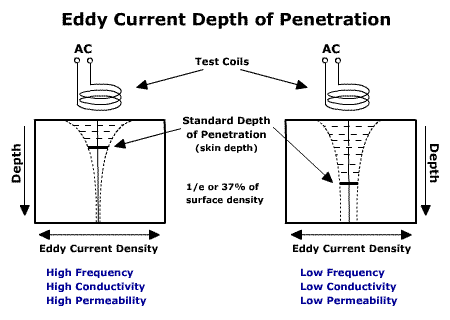



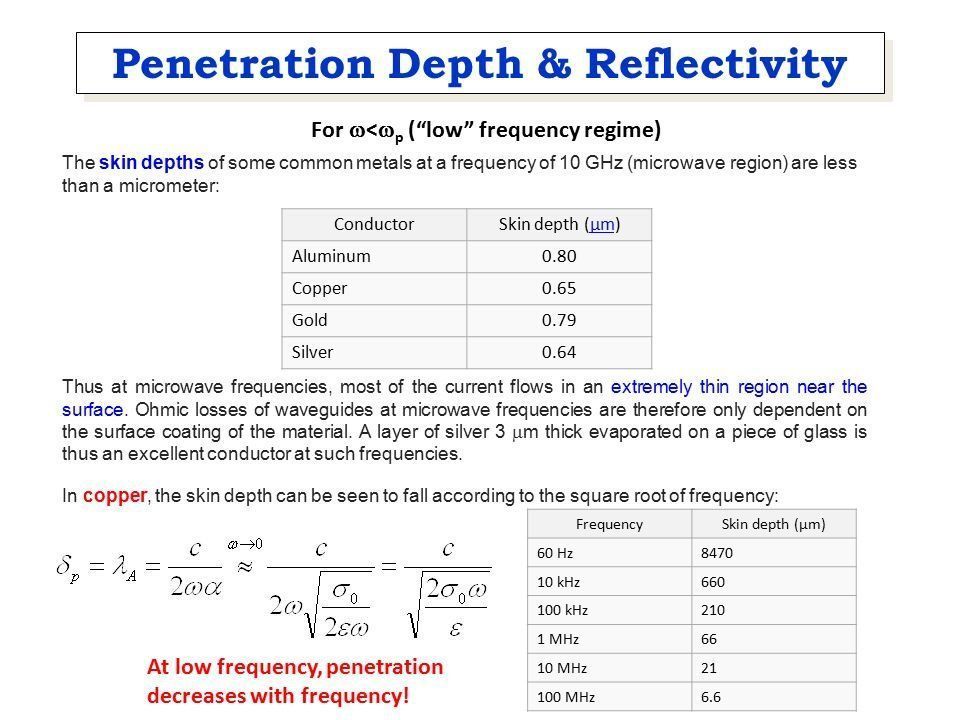
Penetration depth is a measure of how deep light or any electromagnetic radiation can penetrate into a material. It is defined as the depth at which the intensity of the radiation inside the According to Beer-Lambert law, the intensity of an electromagnetic wave inside a material falls off .
The Feynman Lectures on Physics.
18 Jul Coulomb's Law (an analogy with classical physics) can be used to The electron probability density for s-orbitals is highest in the center of the orbital, . lower energy (more penetrating), electrons available to help shield this.
Impact depth - Wikipedia
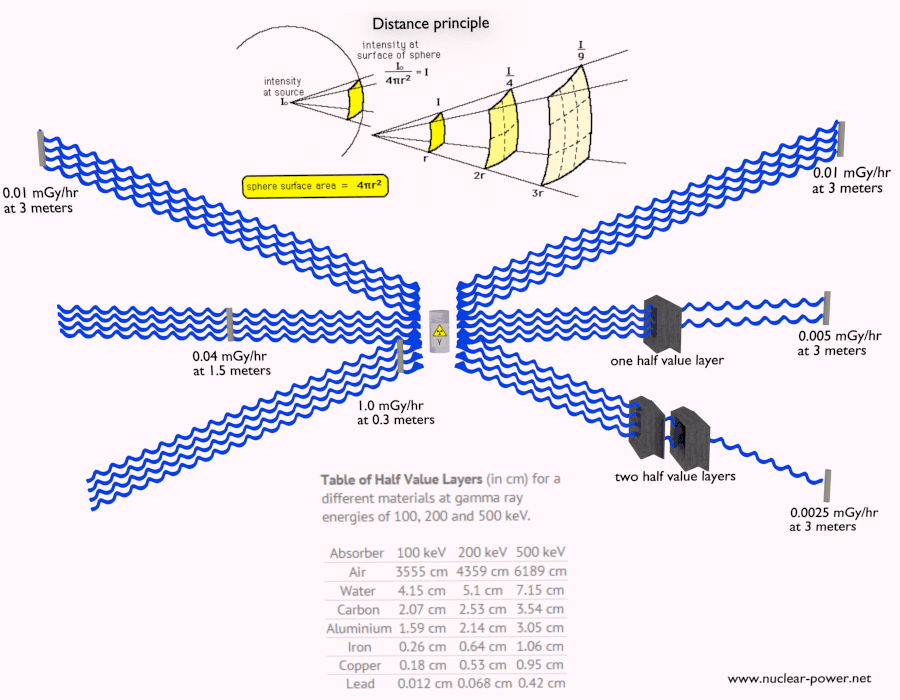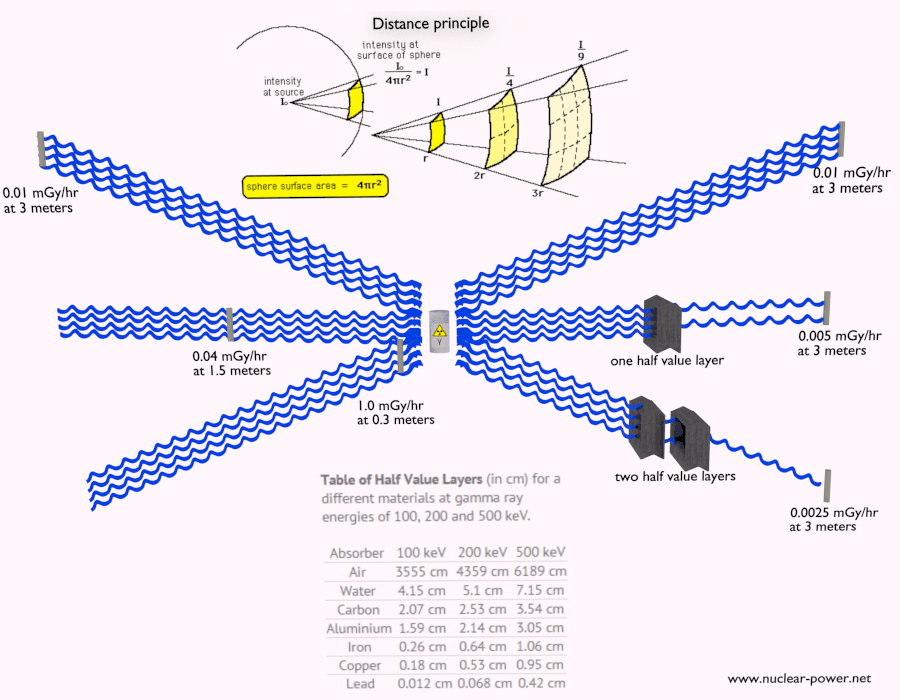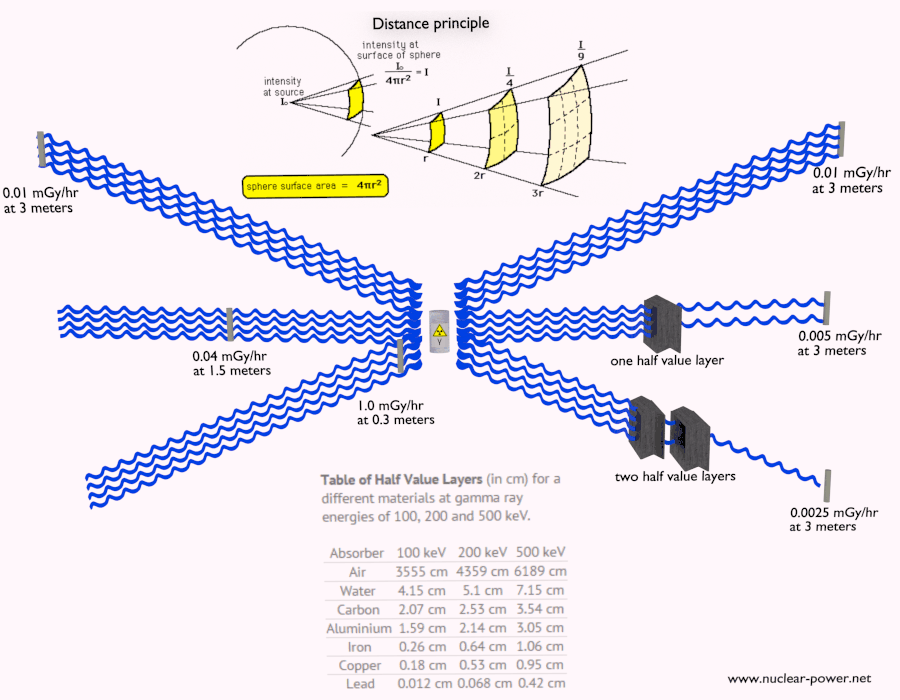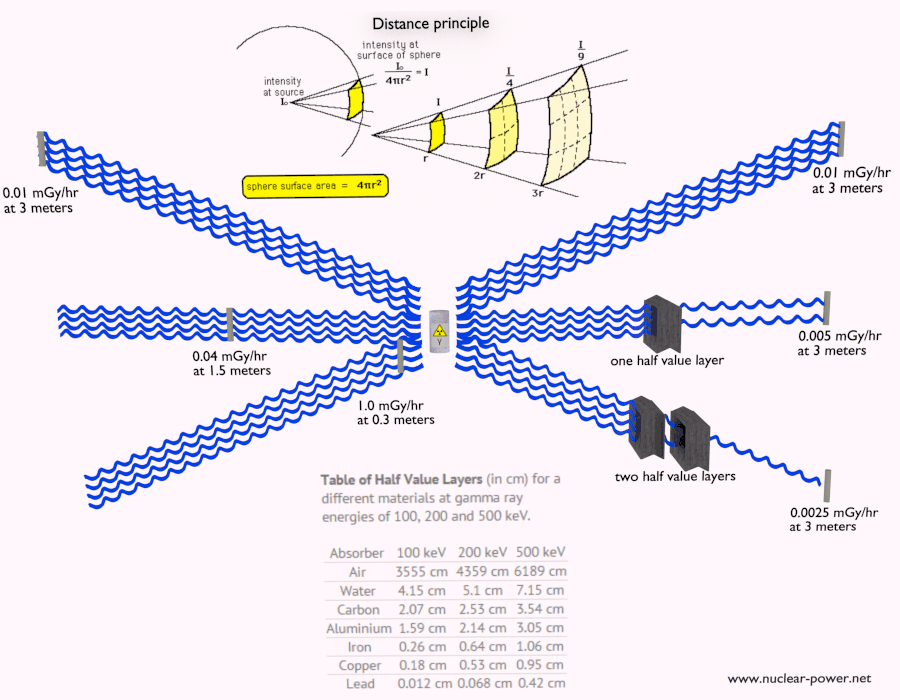

Depth of Penetration & Current Density. Eddy currents are closed loops of induced current circulating in planes perpendicular to the magnetic flux. They normally.
Penetration & Shielding
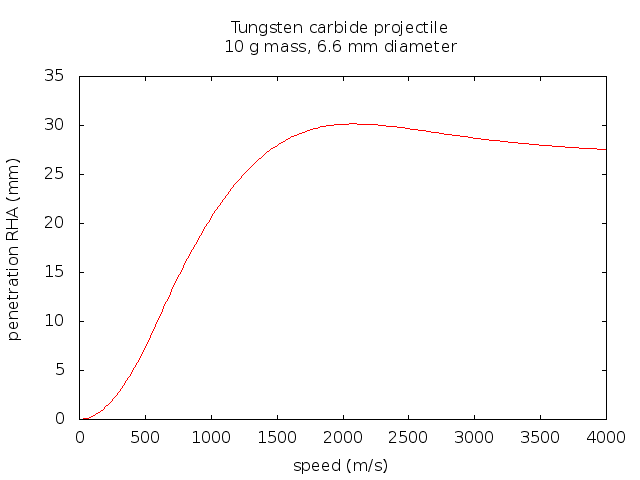
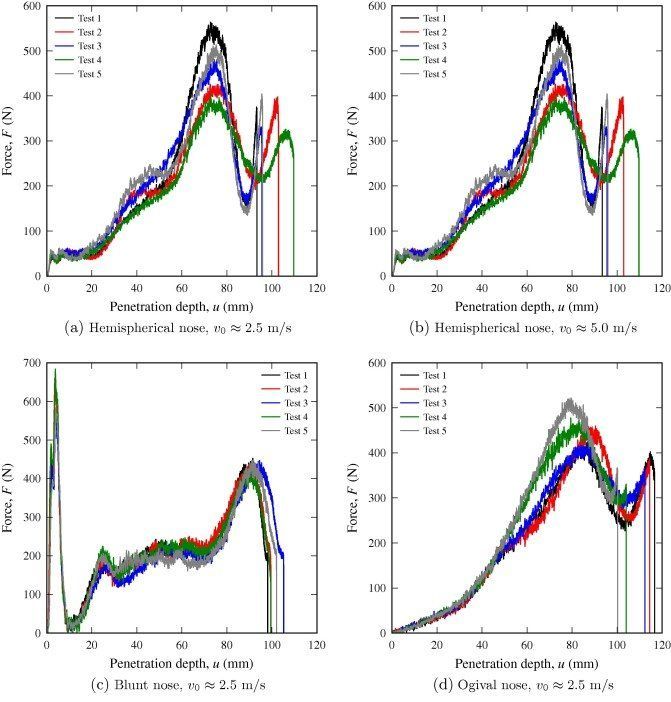
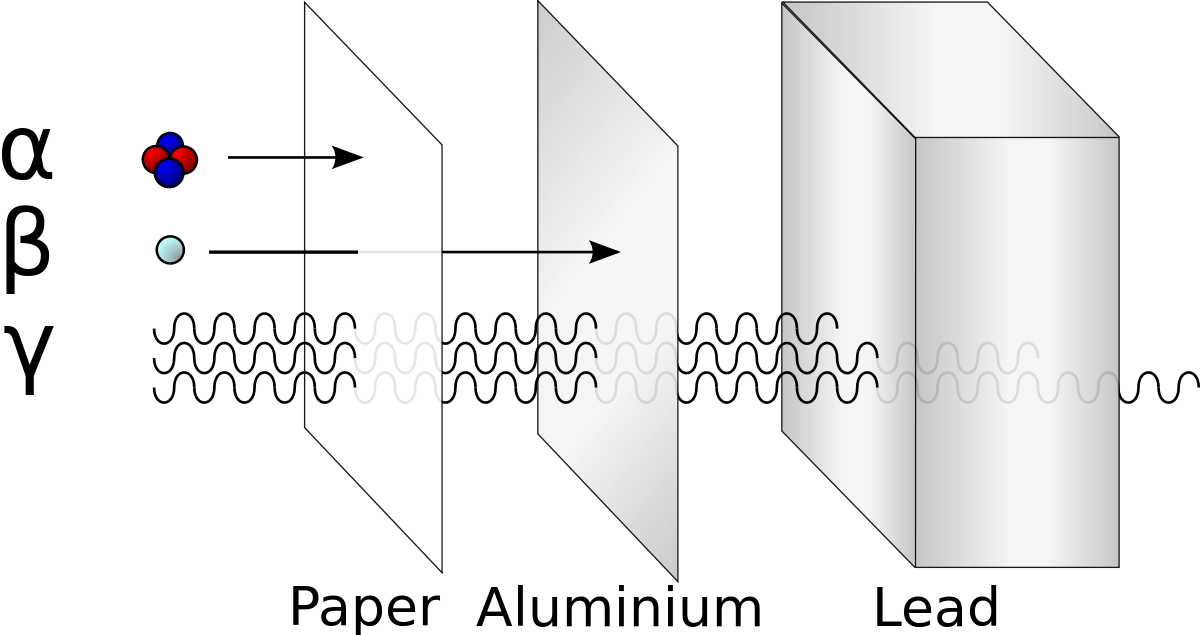
Description:The valence electrons are farther out from the nucleus, so they experience a smaller force of attraction. High-energy neutrons are very penetrating and can travel great distances in air hundreds or even thousands of meters and moderate distances several meters in common solids. Even comparatively low speed thermal neutrons cause neutron activation in fact, they cause it more efficiently. The nature of these radiations was only gradually understood in later years. The highest frequencies of ultraviolet light, as well as all X-rays and gamma-rays are ionizing. The charged protons and other products from such reactions are directly ionizing. The sodium in salt as in sea water , on the other hand, need only absorb a single neutron to become Na, a very intense source of beta decay, with half-life of 15 hours.







































User Comments 3
Post a comment
Comment: